SD WAN - Performance Benefits
In this post we discuss how SD WAN brings a number of benefits to the performance of a WAN. We show how SD WAN can deliver better performance from twin circuits, how it can improve application performance with real time application routing and path conditioning, and how it can allow you to remove Class of Service from your underlying MPLS or VPLS network.
Read the full Guide to SD WAN Benefits here
Incidentally, if you are a large enterprise managing your own WAN then you should see these benefits directly. If you have bought a Managed WAN then it is likely that your service provider will see some of them rather than you directly. Nonetheless, it is to be hoped that you would enjoy a better service as a result.
SD WAN can deliver better performance from twin circuits than a traditional WAN
Traditional networks frequently employ backup circuits for important sites, and these are often employed in passive mode; switched in when the main circuit fails. Intuitively we can see that it is inefficient (and thus costly) to have one circuit sized for the total traffic requirements of a site and another not used at all in normal circumstances. This is especially the case for resilient circuits where the (normally unused) backup circuit has the same bandwidth as the active circuit.
So, how does SD WAN help?
Well, for sites with more than one circuit, SD WAN makes it easier to use both circuits actively, rather than having one active and one passive. Since both circuits are sharing the load, better performance can be achieved from a given circuit Alternatively, the port speeds for both circuits could be lowered to reduce cost while achieving the same performance.
So how does SD WAN make it easier?
To put it the other way around: why is it more difficult to use both circuits in a traditional WAN?
- Well, a traditional WAN can indeed use both circuits, but generally it’s a case of Application 1 using Circuit 1 and Application 2 using Circuit 2.
- If Circuit 1 is congested then Application 1 doesn’t use Circuit 2, it just drops packets.
- Or it could be that one set of users uses Circuit 1 and another uses Circuit 2 although this is unhelpfully splitting the network.
A traditional MPLS or Ethernet WAN does not use dual circuits intelligently.
- It blindly follows configuration rules, rather than determining the best end-to-end path based on parameters that have been set.
- Site routers are generally set up in an Active/Passive configuration with the Passive circuit only being utilised in the event of a failure of the primary.
SD WAN, on the other hand, will happily use both circuits actively, will consider all of the bandwidth available and monitor spare capacity, therefore using the available bandwidth more intelligently.
Alternatively, the ability of SD WAN to use both circuits gives the option to halve the bandwidth that would otherwise be required on a single active circuit. This should produce cost savings, although it will result lower available bandwidth while one of the circuits is down.
IF YOU WANT TO SEE SOME SPECIFIC COST REDUCTION EXAMPLES, YOU CAN DOWNLOAD OUR ‘SD WAN CIRCUIT COST-REDUCTION ILLUSTRATION’
SD WAN uses real-time application routing to improve performance
With SD WAN, each application can be given its own Service Level Agreement (SLA) with conditions that determine the routing for that particular application. This allows you to maximise the performance of your high priority, performance-sensitive applications.
In more detail:
- A ‘Business Intent’ can be set up for an application, or for a group of applications.
- This is a set of rules that reflects what the business wants to happen in different situations and includes the SLA.
- It could be set up to use any available bandwidth as long as it meets the SLA requirements of the application; or set up to always prefer to use a certain circuit. For voice, it might be set up to use all circuits at the same time.
- The Business Intent then drives the use of the underlying network in real time to achieve the SLAs identified for each application.
It probably goes without saying that for SD WAN to make real-time changes to the routing of your application traffic, it needs more than one route to choose from. Thus, you will need at least two circuits to your sites. These might be MPLS, VPLS, Fibre Internet, Broadband Internet or 4G connections. If you have only one connection, SD WAN will still give you greater end to end visibility of the performance of that route.
Contrasting with this flexible routing, a traditional WAN will only route differently on the loss of a route, not when that route is merely under-performing or congested.
This brings us onto the discussion of ‘Brown outs’, which refer to the degradation, rather than loss of a connection.
- Brown outs typically occur as ‘micro bursts’ which can last for a period of time or be intermittent.
- They can affect any application. However, they will be more noticeable on real-time apps like voice, video and RDP - and users are less accepting of these ones degrading.
- It's likely we wouldn’t see brown outs with standard monitoring metrics since micro bursts would not be seen with standard monitoring parameters.
SD WAN can use a number of techniques, such as Path Conditioning, dynamically to overcome these issues.
On ADSL we expect more frequent brown outs because of the nature of the circuits, especially on long lines. Since only traffic that is tolerant of performance degradation would continue to use the circuit, it’s wise to not have two ADSL circuits to a site if it is a long way from the nearest exchange.
One point to note here though is that unless the performance is reviewed, SD WAN could be masking a problem with the underlying network by routing around it. Of course, depending on your point of view, you might see this as a positive as well as a negative!
Read our full Guide to SD WAN Benefits
SD WAN makes poor quality internet act more like MPLS by use of path conditioning
SD WAN can improve the performance of unstable links, which is particularly useful for voice and for allowing global sites to use local broadband.
Some vendors can overcome the performance issues of the underlying transport rather than simply routing traffic around the problem. This ultimately provides better resource utilization, higher application performance, improved productivity, a better user experience and lower bandwidth costs.
SD WAN can send voice packets down multiple links to overcome any packet loss on an individual link. We’ve been using this for years on our 4G WAN replacement circuits, to make reliable circuits out of multiple 4G connections.
Some vendors use techniques such Forward Error Correction and Packet Order Correction to avoid having to re-transmit packets. Forward Error Correction injects loss recovery packets to fix problems at the far end, and Packet Order Correction re-sequences packets at the far end. These Path Conditioning techniques reduce the number of packet re-transmissions required and allow you to achieve call quality on slower and less reliable connections.
Key Point: However, you need to consider that not only do broadband circuits have lower performance and stability than ethernet based access circuits, they also have poorer fix times when they do fail. While an Ethernet circuit might be fixed within hours, a broadband circuit’s fix-time SLA is usually measured in days.
A cynic might argue that SD WAN vendors are promoting a cheaper and poorer performing access circuit but then then offering to fix the problem they’ve created! However, it is certainly the case that SD WAN gives you more options to select the most appropriate compromise between performance, reliability and cost.
SD WAN can offer Class of Service over the internet
SD WAN creates End to End tunnels and has an awareness of the multiple tunnels that might be on the SD WAN device at each site. This allows the devices to manage the data that is being sent.
A traditional WAN can have Class of Service (CoS) on the router, but the router isn’t aware what other devices are doing, meaning that a video call between Site A and B could be interrupted by a large file being received from Site C.
With SD WAN, the Business Intent Overlays are set up to maintain the performance of an application. If the network isn’t congested and the end to end SLA meets the applications criteria, then the prioritisation doesn’t need to be applied. However, if the network is contended then the SD WAN devices can prioritise the applications as defined in the Business Intent Overlays. It can send a message to the other devices in the network that Application X is to be prioritised and other traffic needs to be limited.
SD WAN can improve MPLS performance without needing CoS
We discussed above that SD WAN employs path conditioning and real time application routing to improve application performance over the internet. This also works for MPLS, which means that SD WAN could let you dispense with running CoS on an MPLS (or indeed a VPLS) network.
How does this help?
Well, to start with, it reduces complexity. CoS adds an extra layer of complexity to set up, and we’ve seen instances in the past when it’s not been deployed properly anyway. If you have multiple MPLS suppliers then there may be different classes used for different purposes. And if you have a mixed network with layer 2, then you’ll be using different markings again for quality of service. With SD WAN and no CoS then performance is set up consistently across all network types.
Secondly it puts application performance into your hands and makes it quicker to make changes. Setting up and changing CoS is done via the Carrier, which means that you have to request it, await their changes and then have the routers configured. With SD WAN it’s a simple process to make a change across the whole network.
Thirdly, it can save cost, which we’ll explore in our Guide to SD WAN Cost Benefits.
SD WAN improves Cloud Application performance by identifying the best route and supporting local internet breakout
Often when a remote site has an MPLS primary and an Internet broadband back-up, the backup is only used when the primary fails and then just creates an IP Sec tunnel to the HQ.
Many companies are either hosting their applications in the cloud or are using cloud-based Software as a Service such as Salesforce or Microsoft Office 365 MS365.
If all traffic has to traverse a central firewall at the HQ/DC then not only does this require more bandwidth at the HQ/DC to trombone the traffic in and out but it also adds more latency meaning poorer performing applications.

With SD WAN the remote site can access MS365, for example, directly via the Internet connection. This will provide a shorter path to the application, meaning improved performance. Secondly, it will remove traffic from the MPLS connection, which potentially can contribute to a smaller port and therefore a cost saving.
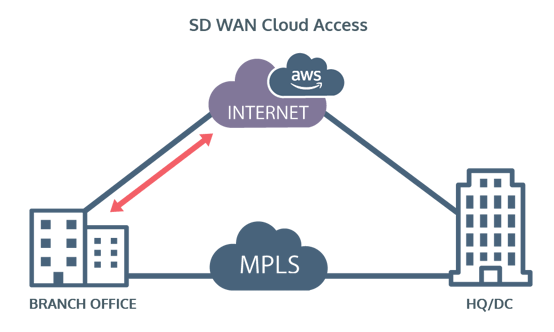
However, if the performance of the local internet circuit deteriorates and the application SLA is not being met then the network can look at the SLA performance of routing the traffic via HQ/DC and decide whether to route that way instead.
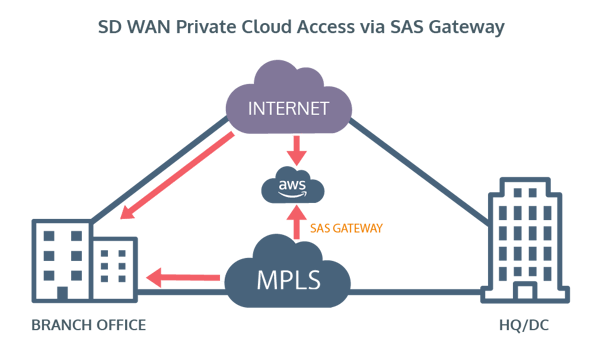
There is a further option to access cloud platforms such as AWS and Azure. That is to have private cloud connectivity from your network.
This would be a third way for the branch site to reach the IaaS platform and it may well have a better SLA than the local Internet break-out. It will depend on geography - which region the Branch site and the IaaS platform reside in. This is usually our preferred method for connecting to Cloud platforms; providing cost effective, high performance through the SAS Gateway.
SD WAN can improve performance by apply appropriate security and routing to recognised apps
Typically, a traditional WAN sends external traffic to the corporate firewall. As more and more applications are run from the internet, this has an increasing impact on performance.
SD WAN can treat known applications such as Microsoft 365 and Salesforce as trusted, and route them direct to the internet or to a web proxy such as Zscaler or Cisco Umbrella. This can reduce latency because there are fewer hops. It also lets you reduce both firewall capacity and bandwidth from the Corporate Firewall.
SD WAN vendors can set up SLA requirements for known applications, and this makes it easier to set up a business intent for them. For example, Silver Peak recognises over 10,000 Apps and has defined SLA requirements for them. It has a ‘first packet IQ’ feature to recognise the traffic from the first packet and route it accordingly.
User groups can have different policies assigned to help manage security and performance
In addition to routing applications differently, groups of users can also have different policies applied.
In the case of two users - one on your guest Wi-Fi, and the other on your corporate LAN, with both trying to reach the same website - an SD WAN router can send the Wi-Fi user’s traffic out to the internet and the Corporate LAN user’s traffic to the Corporate Next Generation Firewall.
In a retail environment, Point of Sales terminals can have their own Business Intent. If this is attacked, then traffic can’t access other parts of the network.
This is possible on a traditional WAN using VLANs, but it is harder to configure.
SD WAN makes applications easier to secure and administer by using DNS rather than IP Addresses.
SD WAN uses URL and DNS to keep updated with changing IP addresses for applications such as Microsoft 365.
By using the URL and DNS, any update to the available ranges of IP Addresses will automatically be known to the SD WAN device.
With a traditional WAN, one has to update the IP Addresses that the firewall will allow inbound traffic from periodically; otherwise it may block MS365 traffic.
SD WAN does this automatically - and instantly.
SD WAN improves the performance of SaaS and IaaS by using virtual devices
SD WAN vendors such as Silver Peak can improve the performance of applications in a cloud environment such as Microsoft Azure, by being able to deploy a licence within the Infrastructure as if it was a piece of hardware on a site. This allows them to consider both ends of the connection rather than just one.
Customers who run standard Internet access to the virtual network alongside Azure ExpressRoute can benefit from Dynamic Path Control (DPC), a feature that enables simultaneous use of multiple underlay transports (e.g. both ExpressRoute and Internet). This allows you to maximise availability, throughput or efficiency, according to the requirements of the application.
SD WAN can make WAN Optimisation easier and cheaper to deploy
Consider a global network which has 10 sites across Asia needing to access a few applications in your HQ. The latency on those links might mean that the applications don’t work very well. High packet loss might mean that the applications are taking up more bandwidth than they need to.
WAN optimisation can increase throughput by overcoming TCP Windowing (which restricts an individual data flow). It can and reduce the demand for data by caching and other methods.
However, with a traditional WAN, separate WAN Optimisation devices would need to be bought, configured, installed and maintained which could make it cost prohibitive for this scenario.
SD WAN allows you to deploy WAN Optimisation purely as software, avoiding these issues. Furthermore, the licence can be apportioned and moved from site to site as needs change, with very little difficulty.
In the example above, a Silver Peak 100Mbps Unity Boost licence would allow 10 Mbps of optimisation at each site and would cost about £4k per annum to improve the performance for all the users at these ten sites.
SD WAN can create secure connections over the internet in a simpler and more flexible way than IP Sec
With SD WAN, key rotation is controlled by the orchestrator whereas with a traditional WAN using IPSEC, this has to be configured on a hub device and has limitations. It's simpler and more flexible with the SD WAN.