How do I troubleshoot VOIP?
When VoIP issues are reported, there are many potential causes for quality issues. If VoIP is new to your business, we have put together a guide to the most common causes of VoIP issues and how to troubleshoot them.
Check Licensing
The first thing to do, but easily missed, is to check that the functionality reported as not working is available with the license that user has.
For example, a user has reported that their call recording functionality is not working. This could be that there is an issue with the call recording setup. However, it could also be that their license does not have call recording enabled. This is a common occurrence when users transfer departments and require different features.
Inspect Equipment
If the issue reported is complete loss of service or intermittent dropping of calls, the issue could lie with the equipment. Depending on your VoIP setup, there could be a plethora of different equipment or very minimal.
It is important to check all equipment is connected correctly. Start with the endpoint. This could be a VoIP handset, a laptop with a softphone installed or a conference device in a meeting room. Check ethernet and power cables are thoroughly connected and if the device is receiving power and internet. If the problem continues, trace the cables back to the point of origin and ensure fully connected here too.
Replace Equipment
If all is connected correctly, the issue could be with the equipment itself. It is recommended with new voice deployments that you purchase some spare handsets to enable you to rapidly test whether the handset is at fault.
If the spare handset does remedy the issue, you can contact your service provider to arrange a replacement for the original. Most VoIP handsets come with a warranty. Check with your service provider for their specific terms around handset replacement.
Other than the physical endpoint, routers and firewalls could be blocking certain functionality on your VoIP service. If the problem has been reported by more than one user, it is best to check your internet and network connectivity.
Check Internet Connection
VoIP is reliant on your internet connection. Therefore, if your internet is down, your VoIP is down. If your internet is performing poorly, your VoIP setup will mirror this.
When internet connectivity suffers an outage, you can redirect incoming calls to be received at another site. This is the reactive option. Usually, VoIP solutions are pre-configured to automatically failover to backup scenarios.
In complex configurations, when business communications are viewed as critical, VoIP solutions are shared across two internet connections. One remains in an idle state until required. This provides a service where your VoIP services automatically kick in on the standby connection. In this scenario, you retain the ability to make outbound calls as well as inbound.
For remote workers, this may seem trickier to diagnose and resolve. However, with MOS (Mean Opinion Scoring) and other monitoring applications included in your VoIP package, you can see where and why devices are performing poorly.
Check Network Configuration
If your internet is performing adequately and the equipment has been checked, your network configuration could be stopping VoIP from performing as it should.
Routers and firewalls stop unwanted and uncommon traffic being passed through your network. If you have not deployed hosted voice over your network in the past, your network will likely be blocking voice traffic. This means users of handsets and soft phones will be unable to make calls. Adjust your network and security settings to allow the new voice traffic.
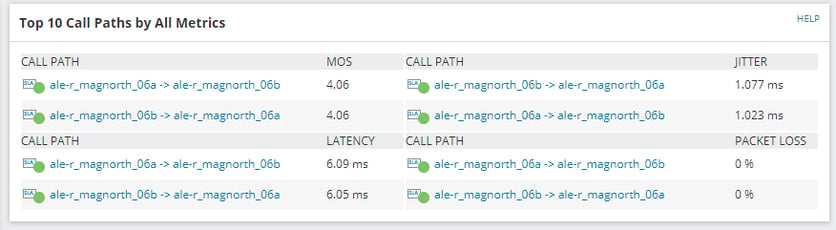
If the issue is quality then jitter, latency and packet loss could be impacting your service. Here are some set levels you adhere to when deploying voice over your network:
Latency: 150ms
Jitter: 100ms
Bandwidth: 100Kbps per concurrent call
With some home broadband routers, these aren’t configured to allow SIP protocols as standard. Home users may need to contact their service provider to change settings or order a replacement router. It is advisable to check this before rolling out VoIP to home users.
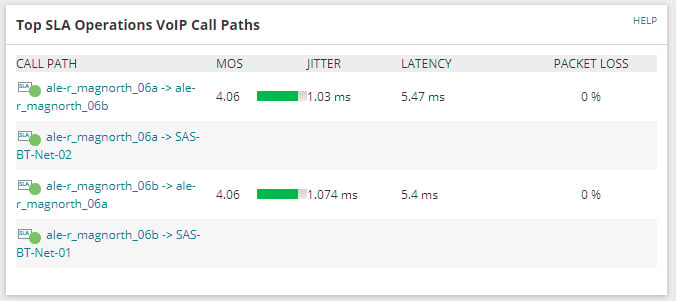
VoIP and Network Monitoring
To avoid having to react to tickets logged by users, you could be taking advantage of proactive monitoring across your network and your VoIP endpoints. At both levels, there is a wide range of persistent monitoring that alerts IT admins when performance dips, so this can be remedied before a user experiences an issue.
Latency, jitter and bandwidth levels can be actively monitored and managed to ensure your VoIP solution is always performing at optimal levels.
Following these steps should remedy most VoIP issues. For anything further than these troubleshooting steps, it may be a deeper issue related to the voice solution.